Property Valuation In Nepal
Property Valuation In Nepal is a critical process that determines the monetary worth of real estate assets within the country’s jurisdiction. This essential procedure affects various aspects of property ownership, including taxation, sales transactions, mortgage financing, and legal disputes. The property valuation system in Nepal has evolved significantly over the years, with recent legislative updates bringing more structure and standardization to the practice.
In Nepal, property valuation is governed by multiple legal frameworks and administered by different government authorities depending on the property type and location. The valuation process considers numerous factors including location, physical characteristics, market trends, and intended use of the property. Understanding how property valuation works in Nepal is crucial for property owners, potential buyers, investors, and legal professionals operating within the Nepalese real estate market.
Legal Framework Governing Property Valuation In Nepal
The property valuation landscape in Nepal is primarily regulated by several key pieces of legislation that establish the legal foundation for valuation practices across the country. The most significant among these is The Nepal Valuation Act, 2019 (2076 BS), which provides comprehensive guidelines on property valuation standards, procedures, and the qualifications of valuers.
This Act is supplemented by The Nepal Valuation Rules, 2020 (2077 BS), which offers detailed implementation guidelines. Additionally, The Land Act, 1964 (2021 BS) and The Land Revenue Act, 1966 (2023 BS) contain provisions relevant to land valuation in Nepal, particularly for taxation purposes.
At the local level, The Local Government Operation Act, 2017 (2074 BS) empowers municipal authorities to conduct property assessments within their jurisdictions. This has become increasingly important after Nepal’s transition to a federal structure, where local governments now have significant autonomy in property valuation matters.
Methods of Property Valuation In Nepal

Property valuation in Nepal employs several recognized methods to determine the fair market value of real estate. These approaches are used singly or in combination, depending on the property type and purpose of valuation.
Comparative Sales Approach
The comparative sales approach is one of the most common methods used in property valuation in Nepal. This method involves comparing the subject property with recently sold similar properties in the same vicinity. Adjustments are made for differences in size, condition, location, and other relevant factors.
Cost Approach
The cost approach calculates the value of a property based on the cost of rebuilding it at current prices, minus depreciation. This method is particularly useful for new properties or those with unique characteristics where comparable sales data is limited.
Income Approach
The income approach is primarily used for income-generating properties such as rental buildings, commercial spaces, and hotels. This method estimates value based on the property’s potential to generate income, considering factors like rental rates, occupancy levels, and operating expenses.
Table: Property Valuation Methods in Nepal and Their Applications
| Valuation Method | Best For | Key Considerations | Common Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| Comparative Sales | Residential properties, land | Market conditions, comparable availability | Property sales, mortgage applications |
| Cost Approach | New buildings, special properties | Construction costs, depreciation | Insurance purposes, new properties |
| Income Approach | Commercial properties, rentals | Rental income, occupancy rates | Investment properties, commercial real estate |
The Property Valuation Process in Nepal
The property valuation process in Nepal follows a systematic approach to ensure accuracy and compliance with legal requirements. Understanding this process is essential for anyone seeking property valuation services in Nepal.
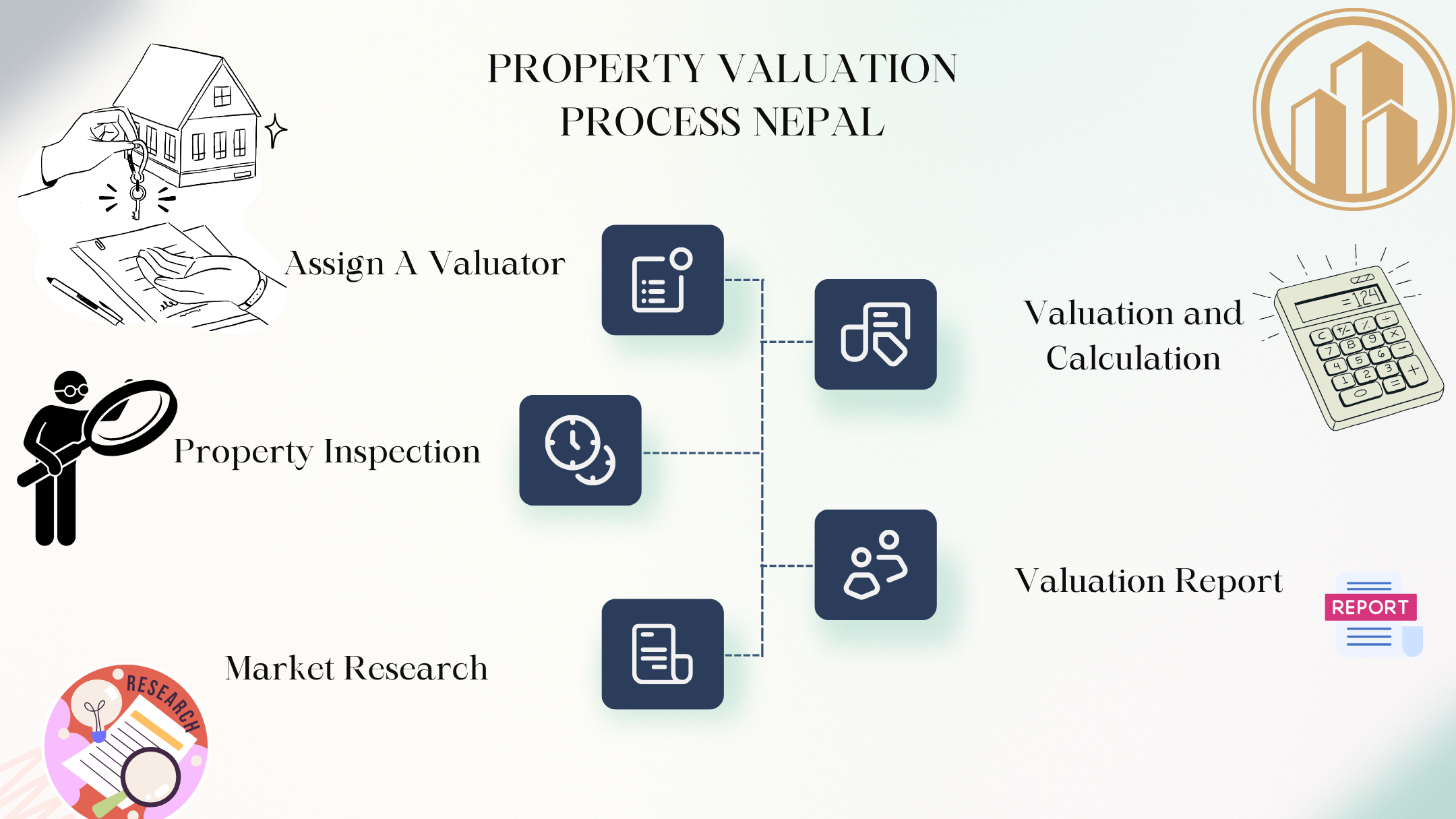
Step 1: Engagement of a Registered Valuer
The first step in the property valuation process is engaging a registered valuer certified by the Nepal government. The Nepal Valuation Act requires that only registered valuers can conduct official valuations for legal and financial purposes.
Step 2: Property Inspection and Data Collection
The valuer conducts a physical inspection of the property, collecting detailed information about its physical characteristics, condition, location, and surrounding area. This includes measurements, photographs, and notes on any features that might affect the property’s value.
Step 3: Market Analysis and Research
The valuer researches market conditions, recent sales of comparable properties, zoning regulations, and any other factors that might influence the property’s value. This research forms the basis for applying the appropriate valuation methods.
Step 4: Valuation Calculation
Using the collected data and research, the valuer applies the relevant valuation methods to calculate the property’s market value. Often, multiple methods are used, and the results are reconciled to arrive at a final valuation.
Step 5: Preparation of Valuation Report
The valuer prepares a comprehensive property valuation report detailing the methodology, findings, and final valuation. This report must comply with the format and content requirements specified in the Nepal Valuation Rules.
Step 6: Certification and Submission
The completed valuation report is certified by the registered valuer and submitted to the requesting party. For official purposes, this report may need to be submitted to relevant government authorities or financial institutions.
Factors Affecting Property Valuation In Nepal
Property valuation in Nepal is influenced by numerous factors that valuers must carefully consider when determining a property’s market value. Understanding these factors is essential for property owners and potential buyers.
Location Factors
Location is perhaps the most significant factor affecting property valuation in Nepal. Properties in prime urban areas like Kathmandu, Pokhara, and Biratnagar typically command higher values than those in rural areas. Within cities, proximity to amenities, road access, neighborhood quality, and future development plans all impact valuation.
Physical Characteristics
The physical attributes of a property significantly influence its valuation. These include:
- Size of the land and building
- Age and condition of structures
- Construction quality and materials used
- Design and architectural features
- Number of rooms and layout efficiency
Legal Factors
Legal considerations play a crucial role in property valuation in Nepal. These include:
- Title status and ownership history
- Zoning regulations and land use restrictions
- Encumbrances, liens, or disputes
- Building permits and code compliance
- Tax status and outstanding dues
Market Conditions
The broader real estate market conditions directly affect property values. Factors such as:
- Supply and demand dynamics
- Economic conditions and growth projections
- Interest rates and financing availability
- Infrastructure development
- Political stability and government policies
Table: Key Factors Affecting Property Valuation in Nepal
| Factor Category | Specific Elements | Impact Level | Valuation Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Location | Neighborhood, accessibility, proximity to amenities | High | Comparative analysis, location premium/discount |
| Physical | Size, condition, construction quality, age | High | Depreciation, replacement cost, functional utility |
| Legal | Title status, zoning, encumbrances | Medium-High | Legal risk assessment, use restrictions |
| Market | Supply/demand, economic conditions, interest rates | Medium | Market trends, absorption rates, investment potential |
Property Valuation for Different Purposes in Nepal
Property valuation in Nepal serves various purposes, each with specific requirements and considerations. The purpose of valuation often determines the methodology, scope, and level of detail required in the valuation process.
Property Valuation for Taxation
One of the most common purposes for property valuation in Nepal is taxation. Local governments use property valuations to determine property tax liabilities. The property valuation for tax purposes follows specific guidelines issued by municipal authorities and often results in values that may differ from market values.
Property Valuation for Mortgage Financing
Financial institutions require property valuation when processing mortgage loan applications. The valuation helps lenders assess the collateral value of the property and determine the loan-to-value ratio. For mortgage purposes, valuations tend to be conservative to protect the lender’s interests.
Property Valuation for Sale and Purchase
In property transactions, valuation in Nepal helps buyers and sellers determine a fair price. While market forces ultimately determine transaction prices, formal valuations provide an objective basis for negotiations and help prevent disputes.
Property Valuation for Legal Disputes
Property valuation is often required in legal disputes such as inheritance cases, divorce settlements, partnership dissolutions, and compensation claims. In these contexts, valuations must withstand legal scrutiny and may be subject to challenge in court.
Property Valuation for Insurance
Insurance companies use property valuation to determine appropriate coverage levels and premium calculations. These valuations typically focus on replacement cost rather than market value.
Property Valuers in Nepal: Qualifications and Registration
The Nepal Valuation Act, 2019 establishes strict requirements for individuals and firms practicing property valuation in Nepal. Understanding these requirements is essential for anyone seeking valuation services or considering a career in this field.
Educational Requirements
To become a registered valuer in Nepal, individuals must possess specific educational qualifications. These typically include:
- Bachelor’s degree in civil engineering, architecture, or related fields
- Specialized training in property valuation
- Knowledge of Nepalese property laws and regulations
Professional Experience
Aspiring valuers must demonstrate relevant professional experience in the real estate or construction sector. The Nepal Valuation Rules specify minimum experience requirements, which vary depending on educational background.
Registration Process
The registration process for property valuers in Nepal involves:
- Submission of application to the Valuation Committee
- Verification of educational qualifications and experience
- Passing of professional examinations
- Payment of registration fees
- Issuance of registration certificate
Code of Conduct
Registered valuers in Nepal must adhere to a strict code of conduct that includes:
- Maintaining independence and objectivity
- Avoiding conflicts of interest
- Following prescribed valuation methodologies
- Maintaining client confidentiality
- Continuing professional development
Recent Developments in Property Valuation In Nepal
The field of property valuation in Nepal has undergone significant changes in recent years, driven by legislative reforms, technological advancements, and evolving market dynamics.
Implementation of the Nepal Valuation Act, 2019
The enactment of the Nepal Valuation Act, 2019 marked a watershed moment for property valuation in Nepal. This legislation introduced standardized practices, enhanced professional requirements, and established a regulatory framework for the valuation profession.
Digital Transformation
The adoption of digital technologies is transforming property valuation practices in Nepal. Geographic Information Systems (GIS), digital mapping, and online databases are increasingly being used to enhance accuracy and efficiency in the valuation process.
Federalism and Local Government
Nepal’s transition to a federal system has significantly impacted property valuation. Local governments now have increased responsibility for property assessment and taxation, leading to variations in valuation practices across different municipalities.
Standardization Efforts
Efforts are underway to standardize property valuation methods across Nepal. This includes the development of uniform valuation standards, guidelines for different property types, and quality assurance mechanisms.
Challenges in Property Valuation In Nepal
Despite recent improvements, property valuation in Nepal faces several challenges that affect accuracy, consistency, and public trust in the system.
Data Scarcity and Reliability
One of the most significant challenges is the scarcity of reliable data on property transactions and market trends. The lack of centralized databases and inconsistent record-keeping makes it difficult for valuers to access accurate information for comparative analysis.
Informal Settlements and Unauthorized Construction
The prevalence of informal settlements and unauthorized constructions poses challenges for property valuation in Nepal. These properties often lack proper documentation and may not comply with building codes, making valuation complex and subjective.
Political Interference
Political interference in the valuation process, particularly for government-related projects and tax assessments, can undermine the objectivity and credibility of property valuations in Nepal.
Limited Professional Capacity
The number of qualified and experienced valuers in Nepal is limited compared to the growing demand for valuation services. This shortage affects the quality and timeliness of valuations across the country.
Outdated Valuation Practices
Many valuers in Nepal still rely on outdated methods and practices that may not accurately reflect current market conditions or international valuation standards.
Future Trends in Property Valuation In Nepal
Looking ahead, several trends are likely to shape the future of property valuation in Nepal as the sector continues to evolve and mature.
Technology Integration
The integration of advanced technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and blockchain is expected to revolutionize property valuation in Nepal. These technologies promise to enhance accuracy, reduce processing time, and increase transparency in valuation processes.
Professionalization of the Sector
The valuation profession in Nepal is likely to become more formalized and professionalized, with stricter licensing requirements, continuing education mandates, and enhanced ethical standards.
Market-Driven Valuations
As Nepal’s real estate market matures, there is likely to be a shift toward more market-driven valuations that better reflect actual transaction prices and investor sentiment.
International Standards Alignment
Nepal’s valuation practices are expected to increasingly align with international standards, facilitating cross-border investments and improving global competitiveness.
Sustainable Development Considerations
Environmental sustainability and climate resilience considerations are likely to become increasingly important factors in property valuation in Nepal, reflecting global trends toward green valuation practices.
Frequently Asked Questions About Property Valuation In Nepal
What is Property Valuation In Nepal?
Property Valuation In Nepal is the systematic process of estimating the monetary worth of real estate assets within Nepal’s jurisdiction. It involves analyzing various factors including location, physical characteristics, market conditions, and legal aspects to determine a property’s market value. This valuation is essential for taxation, sales transactions, mortgage financing, legal disputes, and investment decisions.
What is the legal basis for Property Valuation In Nepal?
The primary legal basis for Property Valuation In Nepal is the Nepal Valuation Act, 2019 (2076 BS), supplemented by the Nepal Valuation Rules, 2020 (2077 BS). Additional relevant legislation includes the Land Act, 1964 (2021 BS), the Land Revenue Act, 1966 (2023 BS), and the Local Government Operation Act, 2017 (2074 BS), which collectively establish the legal framework for property valuation practices in the country.
Where is Property Valuation In Nepal conducted?
Property Valuation In Nepal is conducted throughout the country, with different authorities responsible depending on the property type and purpose. For tax purposes, local governments (municipalities) conduct valuations within their jurisdictions. For mortgage and transaction purposes, registered private valuers perform valuations. Government agencies may also conduct valuations for specific purposes such as infrastructure projects or public acquisitions.
What are the costs of Property Valuation In Nepal?
The costs of Property Valuation In Nepal vary depending on factors such as property type, size, location, complexity, and purpose of valuation. Typically, valuation fees are calculated as a percentage of the property’s value, with minimum fee thresholds set by the Nepal Valuation Association or individual valuers. For residential properties, fees might range from NPR 5,000 to NPR 50,000, while commercial and industrial properties may incur higher fees.
How long does Property Valuation In Nepal take?
The timeframe for Property Valuation In Nepal depends on various factors including property type, location, accessibility, and the purpose of valuation. Generally, a standard residential property valuation may take 3-7 days to complete, while complex commercial properties or specialized valuations may require 2-4 weeks. Urgent valuations can often be expedited for additional fees.
How to challenge Property Valuation In Nepal?
To challenge a Property Valuation In Nepal, particularly for tax purposes, property owners can file an appeal with the relevant municipal authority within the specified timeframe, usually 35 days from the valuation notice. The appeal should include supporting evidence such as recent sales data of comparable properties, independent valuation reports, or documentation of property defects that might affect value. For other types of valuations, disputes may be resolved through negotiation, mediation, or court proceedings.
What qualifications do Property Valuers In Nepal need?
Property Valuers In Nepal must be registered with the Valuation Committee established under the Nepal Valuation Act, 2019. Qualifications typically include a bachelor’s degree in civil engineering, architecture, or related fields, professional experience in the real estate or construction sector, specialized training in property valuation, and successful completion of professional examinations. Registered valuers must also adhere to a strict code of conduct and participate in continuing professional development.
How often should Property Valuation In Nepal be updated?
The frequency of Property Valuation In Nepal updates depends on the purpose and local regulations. For tax purposes, municipal authorities typically reassess properties every 5-10 years, though this varies by municipality. For mortgage financing, valuations are usually valid for 3-6 months. Property owners may also seek updated valuations when significant changes occur to the property or market conditions, such as major renovations, infrastructure developments, or substantial market shifts.
What is the difference between market value and assessed value in Property Valuation In Nepal?
In Property Valuation In Nepal, market value represents the estimated amount for which a property should exchange on the date of valuation between a willing buyer and a willing seller in an arm’s-length transaction. Assessed value, on the other hand, is the value determined by local government authorities for taxation purposes. Assessed values are often calculated using mass appraisal techniques and may be set at a percentage of market value, depending on local regulations and practices.
How has federalism affected Property Valuation In Nepal?
The implementation of federalism has significantly impacted Property Valuation In Nepal by transferring many valuation responsibilities to local governments. Municipalities now have increased autonomy in property assessment and taxation, leading to variations in valuation practices across different jurisdictions. This decentralization has created challenges in standardization but also opportunities for more localized and context-specific valuation approaches that better reflect local market conditions.
Conclusion: The Importance of Professional Property Valuation In Nepal
Property Valuation In Nepal serves as a cornerstone of the real estate sector, providing essential information for transactions, taxation, legal proceedings, and investment decisions. As Nepal’s real estate market continues to develop and mature, the importance of accurate, transparent, and standardized property valuations cannot be overstated.
For property owners, buyers, investors, and legal professionals, engaging qualified registered valuers ensures that valuations are conducted in accordance with legal requirements and professional standards. This not only protects individual interests but also contributes to the overall health and integrity of Nepal’s real estate market.
As the country moves forward with legislative reforms, technological advancements, and professional capacity building, the property valuation sector in Nepal is poised for significant growth and improvement. By staying informed about these developments and working with qualified professionals, stakeholders can navigate the complexities of property valuation with confidence and achieve their real estate objectives effectively.
For professional Property Valuation In Nepal services that comply with all legal requirements and industry standards, contact Company Darta Nepal today. Our team of registered valuers combines extensive local knowledge with international best practices to deliver accurate, reliable, and timely valuation services tailored to your specific needs.

Leave a Reply